What Is AI Video Translation and How It Works
- AI Translator
- AI Video Translator
- AI Video
AI video translation is becoming a core capability for creators and businesses that want to reach global audiences without re-recording content.
Instead of producing the same video multiple times in different languages, AI translation enables a single video to be transformed into multiple localized versions — with translated speech, synchronized lip movement, and subtitles — automatically.
This article explains what AI video translation is, how it works, and why it is increasingly used in modern video workflows.
What Is AI Video Translation?
AI video translation refers to the process of converting spoken content in a video from one language into another using artificial intelligence.
A complete AI translation workflow typically includes:
- Automatic speech recognition (ASR)
- Text translation into a target language
- AI-generated voice output
- Lip-sync or facial motion alignment
- Optional subtitle generation
The goal is not only to translate words, but to preserve meaning, tone, and timing so the video feels natural in the new language.
English Version
Chinese Version (Mandarin)
How AI Video Translation Works
Most AI video translation systems follow a structured pipeline:
- Speech Recognition The system identifies and transcribes spoken dialogue in the original video.
- Language Translation The transcript is translated into the target language while maintaining sentence structure and intent.
- Voice Generation AI generates new audio in the target language, often matching pacing and emotional tone.
- Lip Sync and Timing Alignment Facial movement and timing are adjusted so the translated speech visually matches the speaker.
This process allows one video to scale across regions without manual editing.
Languages Supported Today and What’s Coming Next
Modern AI translation tools often start with a focused language set before expanding.
Current support typically includes:
- Chinese
- English
- Spanish
- Japanese
- Korean
- Portuguese
- French
These languages cover a large portion of global digital audiences. As models improve, expansion toward 19 languages enables broader localization across Europe, Asia, and emerging markets.
Why AI Translation Is Replacing Traditional Video Localization
Traditional localization requires:
- Re-recording audio
- Hiring voice actors
- Manual editing
- Long turnaround times
AI translation dramatically reduces:
- Cost
- Production time
- Operational complexity
This makes global video communication more accessible for creators, educators, and teams.
Final Thoughts
AI video translation is no longer experimental technology. It is a practical solution for scaling video content across languages while maintaining visual and emotional consistency.
As language coverage expands, AI translation will become a standard component of modern video creation workflows.

AI Translate for Global Video Creation: From One Video to Many Languages
AI Translate enables creators to turn a single video into multiple localized versions using automated translation, voice generation, and lip-sync technology. By supporting multiple languages and preserving visual consistency, AI translation helps creators and teams scale video content globally without increasing production complexity.
By Cooper 一 Feb 09, 2026- AI Video
- AI Translator
- AI Video Translator
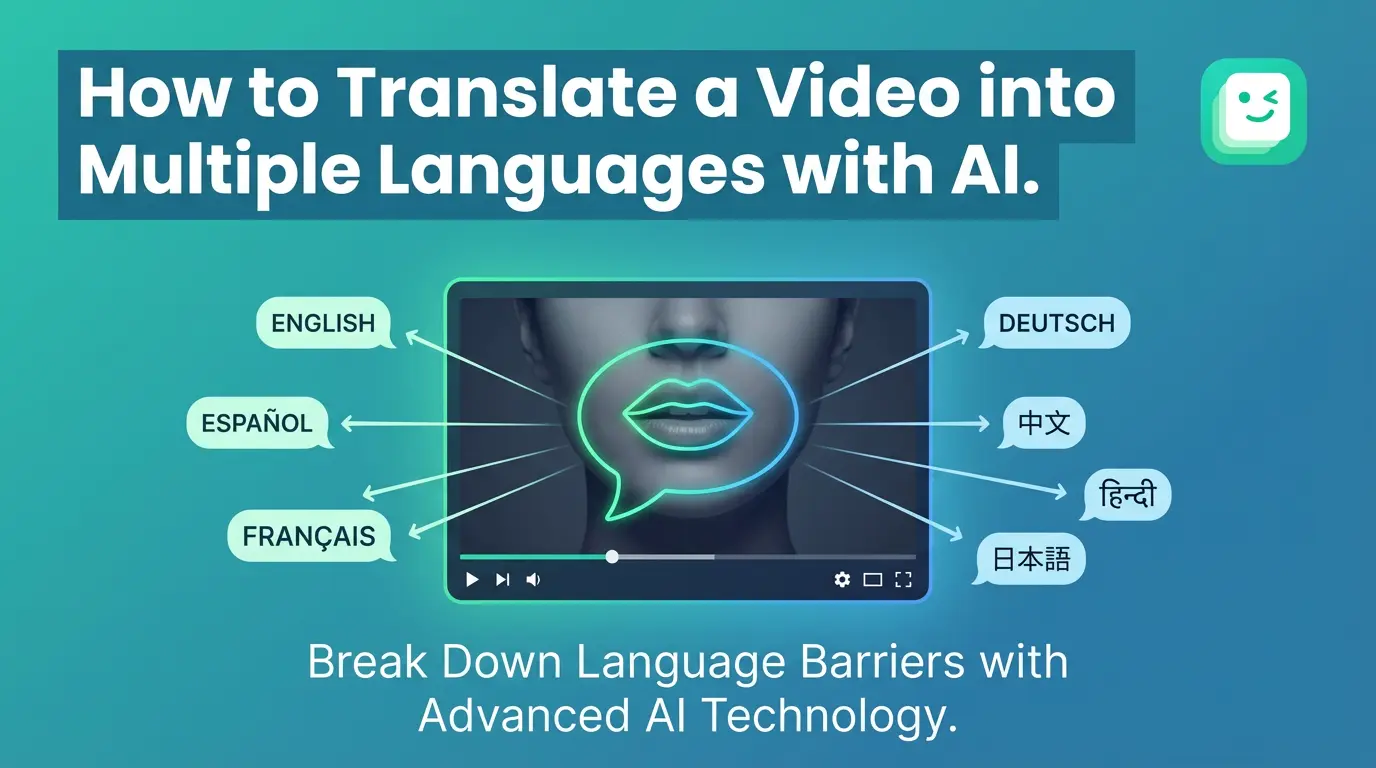
How to Translate a Video into Multiple Languages with AI
To translate a video into multiple languages with AI, users upload a video, select target languages, and generate translated speech with synchronized lip movement. AI video translation removes the need for re-recording and manual editing, enabling creators to produce multilingual videos quickly for education, marketing, and social media.
By Cooper 一 Feb 09, 2026- AI Translator
- AI Video Translator
- Lip-Sync Video

How to Create Winter Olympics–Style Videos with AI
AI text-to-video and image-to-video tools make it possible to create Winter Olympics–style videos without filming or editing. Using written prompts or still images, creators can generate cinematic winter sports motion, snow effects, and athlete-inspired sequences related to the 2026 Winter Olympics. AI video generation is increasingly used for short-form content, concept trailers, and sports-themed storytelling.
By Cooper 一 Feb 09, 2026- Text-to-Video
- AI Video
- Image-to-Video
- X
- Youtube
- Discord
